Share This Article
The journey to conception is a complex process influenced by various factors within the body. One such factor that plays a vital role in fertility and successful conception is the thyroid gland and its hormones. This article explores the significance of thyroid hormones in the process of conception and highlights the importance of thyroid health for couples aiming to start a family.
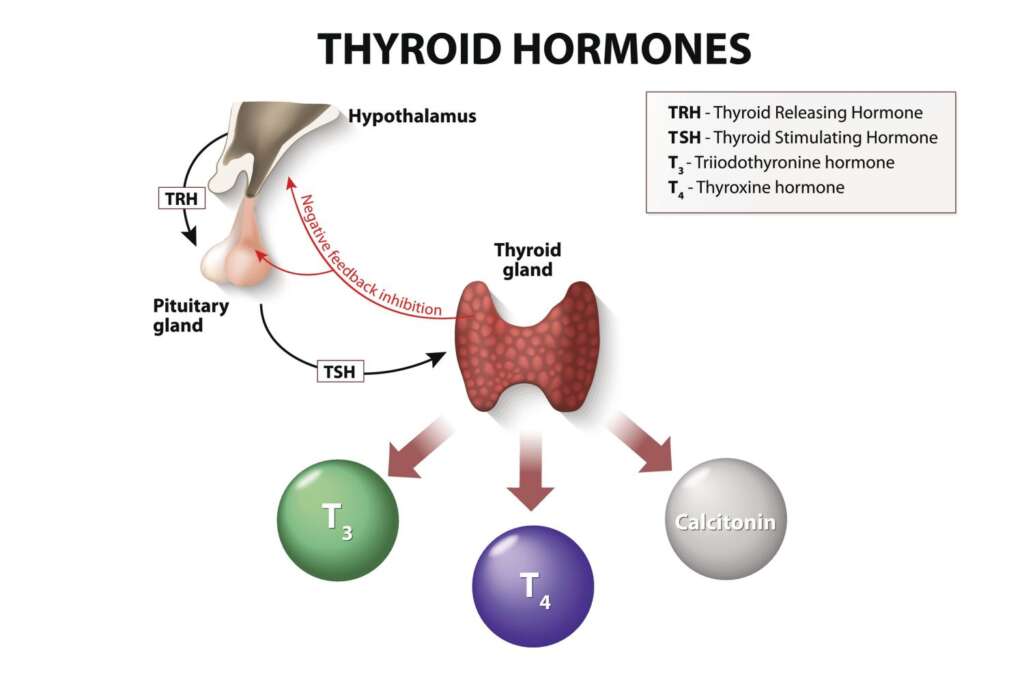
The Thyroid Gland and Its Hormones:
The thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck, produces two essential hormones: thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones play a fundamental role in regulating the body’s metabolism, which affects various bodily functions, including reproductive health.
The Impact of Thyroid Hormones on Conception:
Menstrual Cycle Regulation: Thyroid hormones help regulate the menstrual cycle in women. An imbalance in these hormones can lead to irregular menstrual cycles, which may hinder the ability to predict ovulation accurately.
Ovulation: Adequate thyroid hormone levels are necessary for the proper functioning of the ovaries. Thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism (low thyroid function) or hyperthyroidism (excess thyroid function), can disrupt ovulation and lead to irregular or absent periods.
Follicle Development: Thyroid hormones influence the development of ovarian follicles, which house the maturing eggs. Imbalances can affect the quality and development of these follicles.
Cervical Mucus: Thyroid hormones can influence cervical mucus production and consistency. Changes in cervical mucus can affect sperm transport and viability within the female reproductive tract.
Implantation: Thyroid hormones play a role in the implantation of the fertilized embryo into the uterine lining. An imbalance can affect the receptivity of the uterine lining.
Thyroid Disorders and Fertility:
Hypothyroidism: In cases of hypothyroidism, where the thyroid gland is underactive and doesn’t produce enough hormones, fertility can be impacted. Symptoms may include irregular periods, anovulation (lack of ovulation), and difficulty conceiving.
Hyperthyroidism: Hyperthyroidism, where the thyroid gland is overactive, can also disrupt the menstrual cycle, leading to irregular periods and reduced fertility.
Thyroid Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like Hashimoto’s disease (an autoimmune disorder causing hypothyroidism) and Graves’ disease (an autoimmune disorder causing hyperthyroidism) can affect fertility. Thyroid autoantibodies may interfere with normal reproductive processes.
Thyroid Health and Conception:
Maintaining thyroid health is crucial for couples trying to conceive. Here are some key considerations:
Thyroid Function Testing: If fertility issues are suspected, both partners should consider thyroid function testing. Common tests include measuring levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), T3, and T4.
Thyroid Medication: For individuals with thyroid disorders, appropriate medication and treatment can help normalize thyroid hormone levels and improve fertility.
Consultation with a Specialist: Consulting with a reproductive endocrinologist or fertility specialist is advisable if thyroid issues are suspected or diagnosed. These experts can provide guidance and treatment options tailored to the individual’s needs.
Lifestyle Factors: A healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol, can support thyroid health and overall fertility.
Conclusion:
Thyroid hormones play a crucial role in the complex process of conception. Ensuring that thyroid function is optimal is essential for both men and women seeking to start a family. If there are concerns about thyroid health or its impact on fertility, consulting with healthcare professionals and specialists is recommended. With the right care and attention to thyroid health, many challenges related to fertility can be addressed, increasing the likelihood of successful conception and fulfilling the dream of parenthood.

