The Risks of Consuming Too Much Sugar in Pregnancy
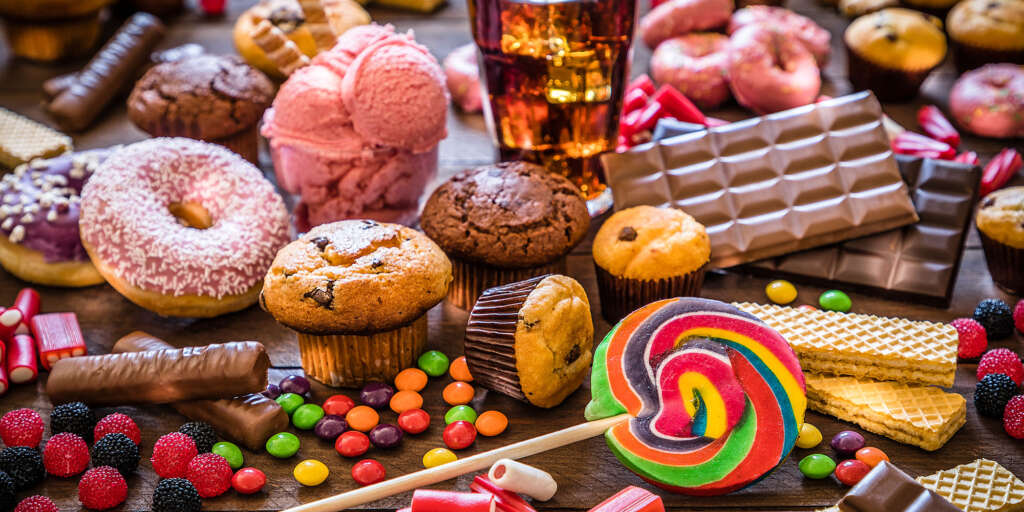

Pregnancy is a time of heightened awareness about health choices, and one crucial aspect is sugar consumption. This article looks into the risks associated with consuming excessive sugar during pregnancy. It discusses potential implications for both the mother and the developing fetus.
Consuming too much sugar during pregnancy can pose significant risks to both the mother and the developing fetus. Excessive sugar intake can lead to gestational diabetes, a condition that increases the risk of complications during pregnancy and birth. It can also contribute to excessive weight gain in the mother, which may lead to preterm birth and complications during delivery. High sugar consumption is linked to an increased likelihood of the baby developing macrosomia or excessive birth weight. This can lead to complications during delivery and an increased risk of childhood obesity. Additionally, a diet high in sugar can impact the baby’s metabolism and increase the risk of them developing type 2 diabetes and other health issues later in life. Therefore, pregnant individuals must monitor and limit their sugar intake. Prioritizing a balanced and nutrient-dense diet is essential. It promotes a healthier pregnancy and better long-term outcomes for both mother and baby.
1. The Impact of Sugar on Maternal Health
a. Blood Sugar Fluctuations
Excessive sugar intake can lead to frequent spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels for expectant mothers. This rollercoaster effect may contribute to gestational diabetes, a condition that can pose risks for both maternal and fetal health.
b. Weight Gain and Increased Risk of Obesity
High sugar consumption is linked to excessive weight gain during pregnancy. Maternal obesity increases the likelihood of complications such as preeclampsia and gestational hypertension. It impacts overall pregnancy outcomes.
Also read: Sweet Conundrum: Exploring The Impact Of Sugar On Fertility
2. Gestational Diabetes and Its Consequences
a. The Connection Between Sugar and Gestational Diabetes
Excessive sugar intake is a major contributor to the development of gestational diabetes. Elevated sugar levels during pregnancy can lead to insulin resistance, causing this condition.
b. Fetal Risks Associated with Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes poses risks to the developing fetus. This includes macrosomia (excessive birth weight), birth injuries, and an increased likelihood of the child developing type 2 diabetes later in life. Proper management is crucial to minimize these risks.
Also read: The Glucose Challenge Test: Screening For Gestational Diabetes
3. Too Much Sugar in Pregnancy: Increased Risk of Preterm Birth
a. Sugar’s Role in Premature Labor
Studies suggest a correlation between high sugar intake and an increased risk of preterm birth. The inflammatory response triggered by excessive sugar consumption may lead to premature labour.
b. Addressing the Link Between Sugar and Preterm Birth
Understanding and addressing the link between sugar intake and preterm birth involves adopting a balanced diet. Monitoring sugar consumption and eating nutrient-dense foods can promote a healthier pregnancy timeline.
4. Impact on Fetal Development
a. Sugar’s Influence on Fetal Growth
Excessive sugar consumption may lead to an overstimulation of fetal insulin production, potentially resulting in accelerated fetal growth. This condition, known as macrosomia, can lead to complications during delivery.
b. Developmental Programming and Long-Term Health
The influence of maternal sugar consumption extends to the child’s long-term health. Emerging research suggests a link between maternal sugar intake during pregnancy and an increased risk of the child developing metabolic and cardiovascular issues in adulthood.
5. Too Much Sugar in Pregnancy: Role in Preeclampsia
a. The Connection Between Sugar and Preeclampsia
Consuming too much sugar may contribute to the development of preeclampsia, a condition characterized by high blood pressure and organ damage. Sugar’s inflammatory effects and impact on blood vessel function may contribute to this complication.
b. Managing Sugar Intake to Reduce Preeclampsia Risk
Managing sugar intake is a modifiable factor in reducing the risk of preeclampsia. Adopting a balanced diet rich in whole foods and low in added sugars supports maternal health. It also reduces the likelihood of developing this complication.
Also read: Understanding Preeclampsia: Symptoms And Prevention
6. Strategies for Reducing Sugar Intake
a. Reading Food Labels and Making Informed Choices
Educating oneself about hidden sugars in processed foods is crucial. Reading food labels and making informed choices empower pregnant women to select nutrient-dense options, reducing the risk of excessive sugar intake.
b. Adopting a Balanced and Varied Diet
A balanced and varied diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, contributes to a healthier pregnancy. This approach provides essential nutrients without the excess sugars often found in processed and sugary snacks.
Also read: How To Include More Vegetables Into Your Diet During Pregnancy
7. Seeking Professional Guidance
a. Regular Prenatal Check-ups and Nutritional Counseling
Regular prenatal check-ups allow doctors to monitor maternal health and provide nutritional counselling. Doctors can offer personalized guidance to ensure optimal sugar intake during pregnancy.
b. Collaborating with a Registered Dietitian
Collaborating with a registered dietitian specializing in maternal nutrition can provide tailored advice. Dietitians can create individualized meal plans, addressing specific nutritional needs while helping pregnant women manage sugar intake.
Understanding the risks associated with consuming too much sugar during pregnancy is a crucial step for expectant mothers. From maternal health implications to fetal development, the impact of sugar is far-reaching. Pregnant women can navigate this sweet challenge by adopting a mindful approach to nutrition. Seeking professional guidance and making informed choices are crucial aspects of this approach.
Pregnancy is a time of heightened awareness about health choices, and one crucial aspect is sugar consumption. This article looks into the risks associated with consuming excessive sugar during pregnancy. It discusses potential implications for both the mother and the developing fetus.
Consuming too much sugar during pregnancy can pose significant risks to both the mother and the developing fetus. Excessive sugar intake can lead to gestational diabetes, a condition that increases the risk of complications during pregnancy and birth. It can also contribute to excessive weight gain in the mother, which may lead to preterm birth and complications during delivery. High sugar consumption is linked to an increased likelihood of the baby developing macrosomia or excessive birth weight. This can lead to complications during delivery and an increased risk of childhood obesity. Additionally, a diet high in sugar can impact the baby’s metabolism and increase the risk of them developing type 2 diabetes and other health issues later in life. Therefore, pregnant individuals must monitor and limit their sugar intake. Prioritizing a balanced and nutrient-dense diet is essential. It promotes a healthier pregnancy and better long-term outcomes for both mother and baby.
1. The Impact of Sugar on Maternal Health
a. Blood Sugar Fluctuations
Excessive sugar intake can lead to frequent spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels for expectant mothers. This rollercoaster effect may contribute to gestational diabetes, a condition that can pose risks for both maternal and fetal health.
b. Weight Gain and Increased Risk of Obesity
High sugar consumption is linked to excessive weight gain during pregnancy. Maternal obesity increases the likelihood of complications such as preeclampsia and gestational hypertension. It impacts overall pregnancy outcomes.
Also read: Sweet Conundrum: Exploring The Impact Of Sugar On Fertility
2. Gestational Diabetes and Its Consequences
a. The Connection Between Sugar and Gestational Diabetes
Excessive sugar intake is a major contributor to the development of gestational diabetes. Elevated sugar levels during pregnancy can lead to insulin resistance, causing this condition.
https://googleads.g.doubleclick.net/pagead/ads?client=ca-pub-1902173858658913&output=html&h=280&adk=1476295454&adf=3168071882&pi=t.aa~a.816165568~i.23~rp.4&w=630&fwrn=4&fwrnh=100&lmt=1706352844&num_ads=1&rafmt=1&armr=3&sem=mc&pwprc=6079120353&ad_type=text_image&format=630×280&url=https%3A%2F%2Fpregatips.com%2Fpregnancy%2Fthree-trimesters%2Fthe-risks-of-consuming-too-much-sugar-in-pregnancy%2F&fwr=0&pra=3&rh=158&rw=630&rpe=1&resp_fmts=3&wgl=1&fa=27&dt=1706352844849&bpp=1&bdt=3544&idt=1&shv=r20240122&mjsv=m202401230101&ptt=9&saldr=aa&abxe=1&cookie=ID%3D2f8fc7ef1a7ecdf3%3AT%3D1706263785%3ART%3D1706352502%3AS%3DALNI_MZyuXdiSGehfKyfHceBpnZkfprZSw&gpic=UID%3D00000cf0806aa197%3AT%3D1706263785%3ART%3D1706352502%3AS%3DALNI_MaCkpkFTi4eViwSCt9Y70yiw6FCxg&eo_id_str=ID%3Dff809c59ba23be30%3AT%3D1706263785%3ART%3D1706352502%3AS%3DAA-AfjYj9DoDRekbumcPft_NoeaR&prev_fmts=0x0%2C1200x280&nras=3&correlator=3693894340447&frm=20&pv=1&ga_vid=1339225893.1706263782&ga_sid=1706352844&ga_hid=1418995049&ga_fc=1&u_tz=330&u_his=3&u_h=768&u_w=1360&u_ah=768&u_aw=1360&u_cd=24&u_sd=1&adx=357&ady=2942&biw=1343&bih=653&scr_x=0&scr_y=608&eid=44759875%2C44759926%2C44759837%2C31080619%2C95320888%2C95321626%2C95322163%2C95323004&oid=2&pvsid=3600661213712933&tmod=1086750062&uas=3&nvt=1&ref=https%3A%2F%2Fpregatips.com%2F&fc=1408&brdim=-8%2C-8%2C-8%2C-8%2C1360%2C0%2C1376%2C784%2C1360%2C653&vis=1&rsz=%7C%7Cs%7C&abl=NS&fu=128&bc=31&bz=1.01&ifi=3&uci=a!3&btvi=1&fsb=1&dtd=13
b. Fetal Risks Associated with Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes poses risks to the developing fetus. This includes macrosomia (excessive birth weight), birth injuries, and an increased likelihood of the child developing type 2 diabetes later in life. Proper management is crucial to minimize these risks.
Also read: The Glucose Challenge Test: Screening For Gestational Diabetes
3. Too Much Sugar in Pregnancy: Increased Risk of Preterm Birth
a. Sugar’s Role in Premature Labor
Studies suggest a correlation between high sugar intake and an increased risk of preterm birth. The inflammatory response triggered by excessive sugar consumption may lead to premature labour.
b. Addressing the Link Between Sugar and Preterm Birth
Understanding and addressing the link between sugar intake and preterm birth involves adopting a balanced diet. Monitoring sugar consumption and eating nutrient-dense foods can promote a healthier pregnancy timeline.
4. Impact on Fetal Development
a. Sugar’s Influence on Fetal Growth
Excessive sugar consumption may lead to an overstimulation of fetal insulin production, potentially resulting in accelerated fetal growth. This condition, known as macrosomia, can lead to complications during delivery.
b. Developmental Programming and Long-Term Health
The influence of maternal sugar consumption extends to the child’s long-term health. Emerging research suggests a link between maternal sugar intake during pregnancy and an increased risk of the child developing metabolic and cardiovascular issues in adulthood.
5. Too Much Sugar in Pregnancy: Role in Preeclampsia
a. The Connection Between Sugar and Preeclampsia
Consuming too much sugar may contribute to the development of preeclampsia, a condition characterized by high blood pressure and organ damage. Sugar’s inflammatory effects and impact on blood vessel function may contribute to this complication.
b. Managing Sugar Intake to Reduce Preeclampsia Risk
Managing sugar intake is a modifiable factor in reducing the risk of preeclampsia. Adopting a balanced diet rich in whole foods and low in added sugars supports maternal health. It also reduces the likelihood of developing this complication.
Also read: Understanding Preeclampsia: Symptoms And Prevention
6. Strategies for Reducing Sugar Intake
a. Reading Food Labels and Making Informed Choices
Educating oneself about hidden sugars in processed foods is crucial. Reading food labels and making informed choices empower pregnant women to select nutrient-dense options, reducing the risk of excessive sugar intake.
b. Adopting a Balanced and Varied Diet
A balanced and varied diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, contributes to a healthier pregnancy. This approach provides essential nutrients without the excess sugars often found in processed and sugary snacks.
Also read: How To Include More Vegetables Into Your Diet During Pregnancy
7. Seeking Professional Guidance
a. Regular Prenatal Check-ups and Nutritional Counseling
Regular prenatal check-ups allow doctors to monitor maternal health and provide nutritional counselling. Doctors can offer personalized guidance to ensure optimal sugar intake during pregnancy.
b. Collaborating with a Registered Dietitian
Collaborating with a registered dietitian specializing in maternal nutrition can provide tailored advice. Dietitians can create individualized meal plans, addressing specific nutritional needs while helping pregnant women manage sugar intake.
Understanding the risks associated with consuming too much sugar during pregnancy is a crucial step for expectant mothers. From maternal health implications to fetal development, the impact of sugar is far-reaching. Pregnant women can navigate this sweet challenge by adopting a mindful approach to nutrition. Seeking professional guidance and making informed choices are crucial aspects of this approach. This ensures a healthier and safer pregnancy journey for themselves and their precious little ones.



