Understanding Maternal Age: Impacts On Fetal Health
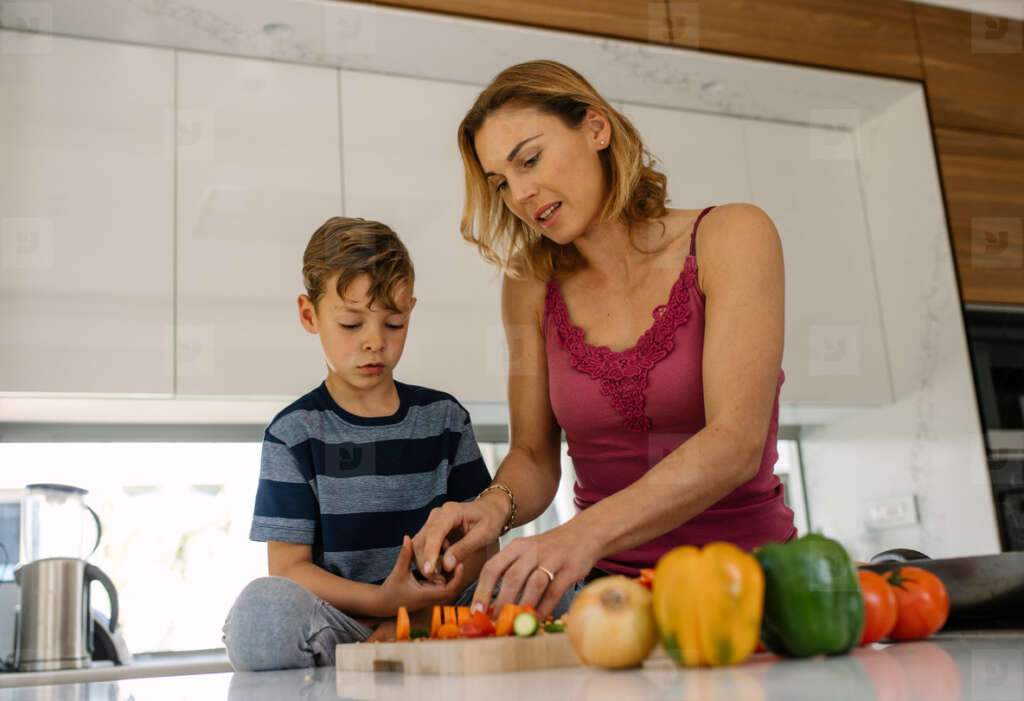

Maternal age plays a significant role in pregnancy outcomes, influencing both the mother’s health and that of the developing fetus. As women choose to start families at various stages of life, it’s essential to understand the potential complications associated with maternal age. In this comprehensive exploration, we look into understanding maternal age-related complications on fetal development and overall pregnancy outcomes.
Maternal age-related complications during pregnancy can have significant effects on the developing fetus. Advanced maternal age, typically considered to be 35 years or older, is associated with a higher risk of various pregnancy-related issues. Older mothers are more likely to experience conditions like gestational diabetes and hypertension. This can eventually lead to complications such as preterm birth, low birth weight, and congenital disabilities in the fetus. Furthermore, the risk of chromosomal abnormalities, particularly Down syndrome, increases with maternal age. This necessitates additional prenatal screening and testing. While many older women have healthy pregnancies and deliver healthy babies, women in this age group need to receive specialized prenatal care. They also need to be aware of the potential risks to ensure the best possible outcome for both mother and baby.
1. Understanding Maternal Age and Fertility
a. Age-Related Changes in Fertility
Maternal age can affect fertility due to age-related changes in the ovaries and the quantity and quality of eggs. As women age, the likelihood of conceiving naturally decreases, leading to an increased reliance on assisted reproductive technologies like in vitro fertilization (IVF).
b. Impact on Egg Quality
Maternal age influences egg quality, with older eggs having a higher risk of chromosomal abnormalities. This can result in conditions such as Down syndrome. The age-related decline in egg quality becomes a crucial factor in the health and development of the fetus.
Also read: Nourishing Fertility: Planning Your Diet For Optimal Egg Quality
2. Risks of Genetic Abnormalities
a. Increased Risk with Advanced Maternal Age
Typically, advanced maternal age, considered to be over 35, increases the risk of genetic abnormalities in the fetus. The chances of chromosomal disorders, such as Down syndrome, rise significantly, emphasizing the importance of genetic counselling and prenatal testing.
b. Chromosomal Abnormalities and Developmental Issues
Genetic abnormalities can lead to developmental issues in the fetus. Conditions like Down syndrome can affect cognitive and physical development, requiring specialized care and support throughout the child’s life. Understanding these risks allows for informed decision-making during pregnancy.
3. Pregnancy Complications in Older Mothers
a. Hypertension and Gestational Diabetes
Maternal age-related complications include an increased risk of gestational hypertension and diabetes. Conditions associated with advanced maternal age, including preeclampsia, premature birth, and macrosomia (considerable birth weight), can impact fetal health. Close monitoring throughout pregnancy is necessary to address potential complications.
b. Effect on Placental Function
Advanced maternal age can affect placental function, compromising the delivery of nutrients and oxygen to the fetus. This can contribute to intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) or macrosomia, both of which pose challenges to the health of the developing fetus.
Also read: Unraveling The Mysteries Of Placental Abruption
4. Impact on Pregnancy Timing
a. Teenage Pregnancies and Prematurity
Teenage pregnancies come with their own set of complications, including a higher risk of preterm birth. Premature babies may face developmental challenges and require specialized medical care to address potential health issues associated with an early arrival.
b. Delayed Childbearing and Pregnancy Risks
Delaying childbearing, often associated with advanced maternal age, introduces its own set of risks. The increased likelihood of infertility, genetic abnormalities, and pregnancy complications necessitates careful planning and monitoring for women conceiving later in life.
Also read: Effects Of Advanced Maternal Age Complications On The Fetus
5. Emotional and Psychological Considerations
a. Teenage Pregnancy and Emotional Readiness
Teenagers may face emotional challenges related to the sudden responsibility of motherhood. Navigating the emotional aspects of pregnancy and ensuring the well-being of both the mother and the developing fetus require crucial support networks and counseling.
b. Emotional Impact of Delayed Childbearing
Delaying motherhood can bring about emotional considerations, including concerns about fertility, societal expectations, and the ability to balance career and family. These emotional stressors can indirectly impact fetal health, highlighting the need for holistic support during pregnancy.
6. Maternal Health and Lifestyle Factors
a. Impact of Maternal Health Habits
Lifestyle factors, such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and poor nutrition, can influence maternal age-related complications. These habits can contribute to pregnancy complications, affecting fetal development and increasing the likelihood of adverse outcomes.
b. The Role of Prenatal Care
Proactive prenatal care is essential for reducing the impact of maternal health habits on fetal well-being. Regular check-ups, a healthy lifestyle, and early intervention can significantly improve pregnancy outcomes, even in the presence of maternal age-related complications.
Also read: The Role Of Prenatal Visits And Tests: What To Expect At The Doctor’s?
7. Strategies for Mitigating Risks
a. Preconception Planning and Counseling
Preconception planning, especially for women of advanced maternal age, involves discussing potential risks with doctors. Guidance on lifestyle changes, genetic testing, and fertility choices empowers women to make informed decisions for a healthier pregnancy.
b. Collaborative Healthcare Approach
A collaborative approach between doctors, genetic counsellors, and mental health professionals is crucial. Addressing maternal age-related complications requires a holistic strategy including physical, emotional, and psychological aspects to optimize fetal health.
In conclusion, understanding maternal age-related complications on fetal health is important for both expectant mothers and doctors. Whether dealing with the challenges of teenage pregnancy or navigating the complexities of delayed childbearing, awareness, and healthcare strategies can reduce risks. Recognizing maternal age-related complications allows for tailored approaches to prenatal care. This ensures the best possible start for both mother and baby on their journey toward a healthy and fulfilling life.



